Blog
NASA Wallops Begins Construction on $103M Causeway Bridge to Support Growing Spaceport Operations
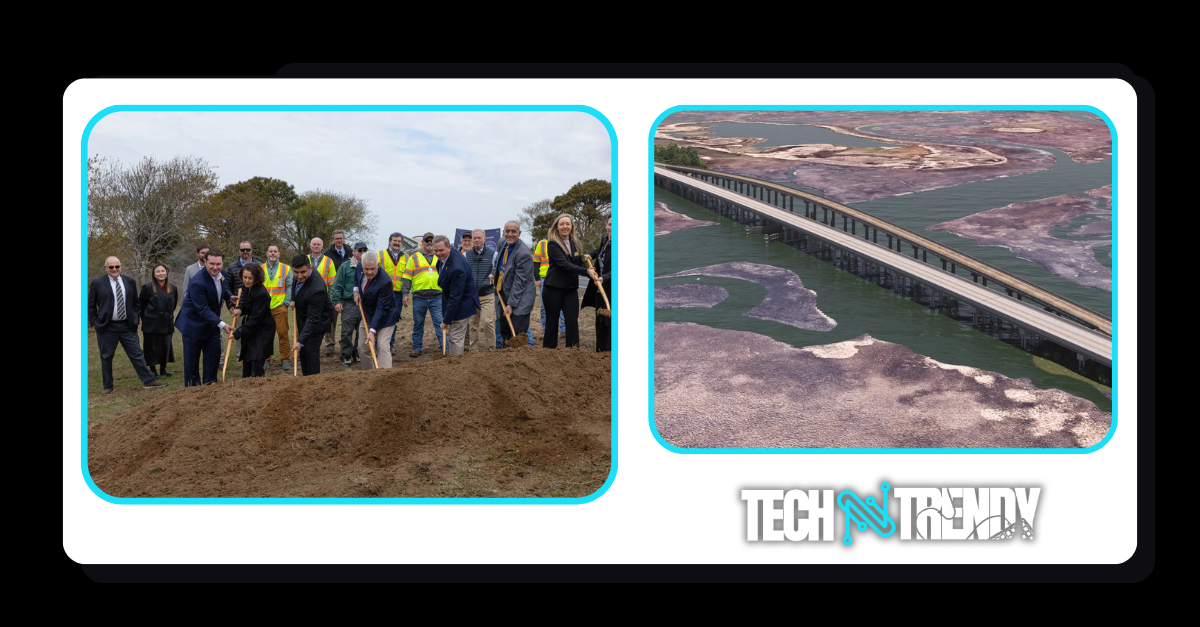

– TechNTrendy.com
Last Updated: April 15, 2025
Key Takeaways:
✔ $103M federal-funded bridge replacement at NASA Wallops Flight Facility
✔ Will support heavier payloads for increased launch cadence (government & commercial)
✔ Construction awarded to Kokosing, completion expected by early 2028
✔ Replaces 65-year-old bridge that’s reached end of service life
✔ Critical infrastructure for Virginia’s expanding space economy
Historic Groundbreaking for Wallops Island’s Lifeline
NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility marked a major milestone on April 14, 2025 with the groundbreaking ceremony for its new causeway bridge—the sole vehicular access point connecting mainland facilities to the launch range on Wallops Island. The event was attended by:
- David Pierce, NASA Wallops Facility Director
- Ray Rubilotta, NASA Goddard Associate Center Director
- Virginia State Senator Bill DeSteph
- Representatives from VA/MD congressional offices
“This bridge enables the science, technology, and national security missions advancing here daily,” said Pierce, noting its role in supporting over 40 annual launches from government and commercial partners like Rocket Lab, Northrop Grumman, and Firefly Aerospace.
Why This $103M Project Matters
1. Replacing Aging Infrastructure
- Current bridge built in 1960 (65 years old)
- Requires frequent repairs due to coastal weather damage
- Weight restrictions limit modern launch equipment transport
2. Designed for Next-Gen Space Operations
| Feature | Old Bridge | New Bridge |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Arched structure | Flat-deck for heavy loads |
| Capacity | 40-ton limit | Unrestricted commercial launch vehicles |
| Lifespan | 50 years (extended) | 75+ year design life |
3. Economic & Strategic Impact
- Supports Virginia Spaceport Authority’s goal of 100+ launches/year by 2030
- Enables transport of larger rockets (e.g., Rocket Lab’s Neutron)
- Strengthens Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport’s (MARS) competitiveness
Construction Timeline & Partners
- Awarded to: Kokosing Construction Company (project portfolio)
- Design oversight: Federal Highway Administration
- Completion target: Early 2028
- Innovations: Corrosion-resistant materials, improved stormwater management
Wallops’ Growing Role in U.S. Spaceflight
The bridge is part of a $2B+ infrastructure overhaul at Wallops, including:
- Launch Pad 0C upgrades for Antares 330 and Neutron rockets
- Payload processing facility expansion (completed 2024)
- AI-powered range safety systems
Recent milestones:
🚀 2024: 14 successful launches (up from 6 in 2020)
🛰️ 2025: First Electron launch from new Pad 0D
🔮 2026: Planned human-rated missions via Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser
What Locals & Businesses Should Know
- Traffic impact: Minimal—construction avoids main commuter routes
- Jobs: 200+ temporary construction roles; 50 permanent ops jobs
- Tourism boost: New visitor center opening 2026 with bridge views
The Big Picture: East Coast Space Race
This project positions Wallops to compete with:
- Cape Canaveral, FL (45+ launches/year)
- Vandenberg, CA (polar orbit focus)
- Spaceport Camden, GA (emerging competitor)
“Virginia is becoming the Silicon Valley of space,” noted Sen. DeSteph, referencing $1.4B in private space investments since 2020.
How to Follow Progress
📅 Webcam updates: Wallops Construction Cam
📰 News alerts: @NASA_Wallops on Twitter
Thoughts? Will this bridge transform East Coast space access? Comment below!
Tech
MITRE’s CVE Program Faces Uncertain Future as Funding Set to Expire
MITRE’s Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) program, a cornerstone of global cybersecurity for 25 years, is at risk of shutting down as its federal funding expires April 16, 2025. This could disrupt vulnerability tracking for millions of organizations worldwide.

Breaking: Cybersecurity’s Vulnerability Backbone at Risk
By TechNTrendy.com
Last Updated: April 16, 2025
MITRE’s Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) program, a cornerstone of global cybersecurity for 25 years, is at risk of shutting down as its federal funding expires April 16, 2025. This could disrupt vulnerability tracking for millions of organizations worldwide.

Why This Matters
✔ Over 250,000 CVEs cataloged since 1999
✔ Critical for patch management, risk assessment, and threat intelligence
✔ CVE Numbering Authorities (CNAs) may soon be unable to assign new IDs
✔ No clear successor program announced
What’s Happening?
- Funding contract expires April 16 (confirmed via internal MITRE letter)
- CWE (Common Weakness Enumeration) program also affected
- Historical CVE database will remain on GitHub, but new assignments may halt
- Centralized MITRE CVE repository could disappear, fragmenting vulnerability data
“This creates massive uncertainty—without CVEs, we lose a universal language for vulnerabilities.”
— Brian Krebs, Cybersecurity Journalist
Potential Impact
| Sector | Risk |
|---|---|
| Enterprises | Slower vulnerability patching, inconsistent tracking |
| Security Vendors | Need alternative databases, possible coverage gaps |
| Researchers | Difficulty disclosing flaws without standard IDs |
| Government | Weakened NVD (National Vulnerability Database) |
Will Vulnerabilities Still Be Tracked?
- Vendors may issue advisories without CVEs
- Alternative databases could emerge (e.g., VulnDB, OSV)
- Tenable, Rapid7, others say they’ll adapt—but fragmentation is likely
What’s Next?
- Last-minute funding extension? (Unlikely per sources)
- NIST may take over, but no official plan yet
- Security firms preparing contingency plans
🔗 Follow Live Updates: MITRE CVE Status Page
Tenable’s Response
As a CVE Numbering Authority (CNA), Tenable assures customers:
✅ Vulnerability scanning will continue (uses multiple sources)
✅ Reserved CVE blocks will help short-term
✅ Research advisories will still publish
“We don’t rely solely on MITRE—but losing CVEs makes defense harder.”
— Tenable Research Team
The Bigger Picture
The CVE program’s potential collapse highlights:
🔴 Over-reliance on a single, underfunded system
🔴 Need for decentralized, resilient alternatives
🔴 Growing gaps in federal cybersecurity support
What Can You Do?
- Monitor vendor advisories directly (not just CVE lists)
- Push for congressional action (Contact legislators)
- Prepare internal tracking systems for non-CVE vulnerabilities
Will the cybersecurity community rally to save CVE? Share your thoughts below.
Blog
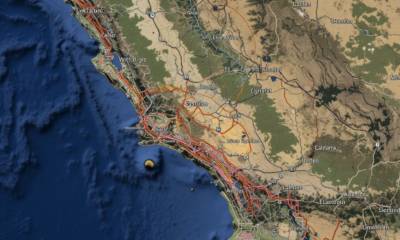
Magnitude 5.2 Earthquake Shakes Southern California; Aftershocks Rattle San Diego Region
– TechNTrendy.com
Last Updated: April 15, 2025
A magnitude 5.2 earthquake struck near Julian, California, early Monday morning, sending tremors across San Diego, Los Angeles, and Long Beach. The quake was followed by multiple aftershocks, including a 4.0 magnitude tremor, keeping residents on edge.
Key Details of the Earthquake
📍 Epicenter: 2.5 miles south of Julian, CA
⏰ Time: 10:00 AM PDT (local time)
📏 Depth: ~8 miles
🌍 Felt Across: San Diego, Riverside, Orange County, and parts of LA

Aftershocks & Immediate Impacts
- 6+ aftershocks recorded, strongest at M4.0
- Boulders dislodged onto Highway 76 (Warner Springs)
- No major injuries or structural damage reported (San Diego Sheriff’s Office)
- No tsunami threat (U.S. National Tsunami Warning Center)
Eyewitness Accounts: “It Felt Like a Massive Explosion”
- John Carneiro (Julian resident):“It shook everything for 10 seconds—like the biggest rumble you could imagine.”
- San Diego resident on social media:“My whole apartment swayed. My dog freaked out and hid under the bed.”
📹 Watch: Security camera footage captures shaking
Why Did This Earthquake Happen?
Southern California sits on multiple active fault lines, including:
- Elsinore Fault Zone (near Julian)
- San Jacinto Fault
- San Andreas Fault (further north)
🔎 USGS Insight:
“This was a moderate shallow quake—common for the region. Aftershocks may continue for days.”
How Southern California Responded
✔ CHP deployed crews to clear rocks on Highway 76
✔ San Diego Office of Emergency Services issued safety reminders
✔ No power outages or major disruptions reported
Earthquake Preparedness Tips
✅ Drop, Cover, Hold On during shaking
✅ Secure heavy furniture & appliances
✅ Keep emergency kits (water, flashlight, first aid)
✅ Sign up for local alerts (San Diego Alert)
Could a Bigger Quake Follow?
- USGS estimates a 5% chance of a stronger quake in the next week
- Most likely scenario: Decreasing aftershocks over 3-7 days
📊 Historical Context:
- 2024: M4.6 near Anza, CA
- 2019: M7.1 Ridgecrest quake (strongest in 20 years)
Final Update: What’s Next?
Authorities continue monitoring aftershocks. Residents should:
- Check homes for gas leaks or cracks
- Avoid mountain roads (possible rockfall)
- Stay updated via USGS Earthquake Map
Were you affected? Share your experience in the comments!
Tech
Optical Computing: The Light-Powered Future of AI and Energy-Efficient Processing
– TechNTrendy.com
Artificial intelligence (AI) is advancing rapidly, but its massive energy demands are becoming a growing concern. Could the solution lie in light-powered computer chips?
Two groundbreaking studies published in Nature suggest that optical computing—using light instead of electricity to process data—could revolutionize AI by making it faster, more efficient, and less power-hungry.
Let’s dive into how this technology works, its current breakthroughs, and whether it can truly replace traditional silicon chips in the AI era.

Why Optical Computing? The Energy Crisis in AI
AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude require massive computational power, leading to skyrocketing energy costs:
- Training a single large language model (LLM) can consume as much electricity as thousands of homes in a year.
- Data centers already account for ~2% of global electricity use, and AI is accelerating this demand.
Traditional silicon-based chips are hitting their limits:
✔ Slowing performance gains (Moore’s Law is fading).
✔ Overheating issues (requiring complex cooling systems).
✔ Energy inefficiency (electrons generate heat as they move).
Optical computing could be the answer—processing data at the speed of light while drastically cutting energy use.
Breakthrough #1: AI-Powered Optical Chips Play Pac-Man & Generate Text
A team from Lightmatter demonstrated the first optical processor running AI models, achieving:
✅ Playing Pac-Man using reinforcement learning.
✅ Generating human-like text (similar to ChatGPT).
✅ Classifying movie reviews as positive or negative.
Their chip combines photonic circuits with traditional electronics, proving that light-based AI is possible.
Breakthrough #2: Solving Complex Problems 460x Faster
Another study by Lightelligence (Singapore) introduced PACE, an optical computer that:
🚀 Reduced computing latency from 2,300 nanoseconds to just 5ns—460x faster than conventional systems.
🔍 Solved complex optimization problems (used in logistics, finance, and AI training) in a fraction of the time.
How Does Optical Computing Work?
Unlike traditional chips that rely on electrons, optical computers use photons (light particles) to:
✔ Transmit data (like fiber-optic internet).
✔ Process calculations (using lasers, lenses, and prisms).
✔ Store information (via optical memory components).
Key Advantages Over Traditional Chips
| Feature | Electronic Chips | Optical Chips |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Limited by electron movement | Near light-speed processing |
| Energy Use | High (needs cooling) | Low (minimal heat) |
| Scalability | Hitting physical limits | Still improving |
| Accuracy | Extremely precise | Improving, but not perfect |
The Big Challenge: Can We Scale Optical Computing?
Despite the promise, optical computing faces hurdles:
🔹 Bulky Systems – Current prototypes are larger than smartphones; scaling up may require football-field-sized setups.
🔹 Signal Loss – Light can weaken over distances, requiring signal boosters.
🔹 Hybrid Needs – Most systems still rely on some electronic components, limiting full efficiency gains.
Dr. Akram Youssry (RMIT) warns:
“If optical computers end up being the size of a stadium, companies might stick with compact electronic chips—even if they’re slower.”
Will Optical Chips Replace Traditional Computers?
Experts believe optical computing won’t fully replace electronics but will specialize in AI and high-performance tasks:
- AI data centers could adopt hybrid systems.
- Quantum computing may integrate photonics for faster operations.
- Edge AI devices (like smartphones) might use optical co-processors.
Prof. Geoff Webb (Monash University) adds:
“AI’s energy costs are in the billions. Even a 10% efficiency gain would save massive resources.”
The Future: A More Efficient AI Revolution?
While optical computing is still evolving, the latest studies prove:
✅ AI can run on light-based processors.
✅ Speed improvements are massive (460x faster in some cases).
✅ Energy savings could make AI more sustainable.
But there’s a catch:
- Efficiency gains might just lead to more AI usage (Jevons Paradox).
- Full-scale adoption could take 5–10 years.
Final Thoughts: A Brighter (and Faster) Computing Future
Optical computing is no longer just sci-fi—it’s here, and it works. While challenges remain, the potential for faster, greener AI is undeniable.
What’s next?
🔹 Smaller, more efficient optical chips
🔹 Hybrid electronic-photonic systems
🔹 Big Tech investing heavily (Google, Meta, NVIDIA already exploring photonics)
Would you trust an AI powered by light? Let us know in the comments!
post 7. #2557D
-
 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months agoiPhone 17 Air: The Thinnest iPhone Ever? Latest Leaks, Specs & Design Details
-

 Ai5 months ago
Ai5 months agoGlobal Backlash: Over 50,000 Creatives Condemn Unlicensed AI Training in Landmark Petition
-
 Blog5 months ago
Blog5 months agoMagnitude 5.2 Earthquake Shakes Southern California; Aftershocks Rattle San Diego Region
-

 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months agoMITRE’s CVE Program Faces Uncertain Future as Funding Set to Expire
-

 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months agoOptical Computing: The Light-Powered Future of AI and Energy-Efficient Processing
-

 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months agoTrilobio: Revolutionizing Lab Automation with Modular, Affordable Robotics
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoUnlock 58% Gains? Decoding Wall Street’s Nvidia Stock Outlook
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoBill Gates-Backed Arnergy Secures $18M to Expand Solar Access in Nigeria Amid Energy Crisis

